ARBAT & Flexible Claudified Architecture for 5G & beyond
The expansion of the service scope of cellular networks to include a wide variety of services such as mobile broadband, Internet of Things, and mission-critical machine-type communications has significantly shaped the evolution towards 5G and beyond systems. In order to meet the demand of modern services, the WNL team developed a flexible network architecture for QoE-aware communications for 5G systems and beyond called ARBAT. The WNL chose this name in honor of street Arbat in Moscow, the most famous and marvelous in the city.
In addition to the beautiful name, ARBAT has all important properties to meet divergent or even mutually exclusive technical requirements for 5G network such as
- Adaptability and Flexibility to help ARBAT to suit a variety of use cases right from eMBB to URLLC;
- Scalability to support a large number of users with different needs;
- Reliability to reassign the functionality of overloaded devices to the other without any service degradation;
- Backward Compatibility and Multiple RAT support to unite devices with various radio access technology under a single framework
- High energy efficiency to minimize energy consumption.
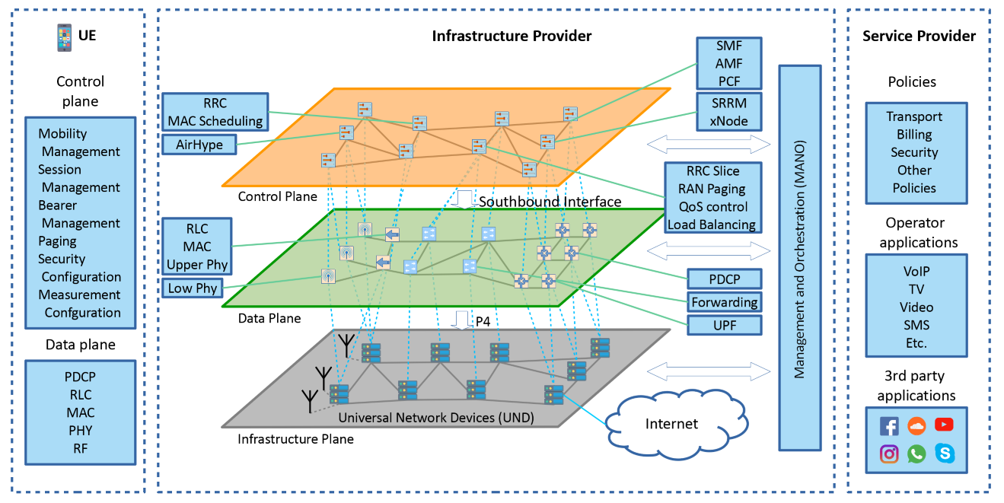
The main feature that provides ARBAT with the above properties is brand new flat architecture with Unified Network Device as a primary building block. Using the Virtual Network Function Virtualization concept, each UND has computational resources to run network functions as software. ARBAT also applies a software-defined network concept, and Data Plane and Control Plane are separated and run on different UNDs. Therefore, UND represents a different context for each network slice. For example, a UND can run only PHY VNFs for an eMBB slice, and almost all VNFs for URLLC slice. Consequently, due to UND, ARBAT unifies Core Network and Radio Access Network in the same framework which increases the adaptability and scalability of the network.
To enable QoE-aware resource management, ARBAT incorporates the xStream platform developed by the WNL team. This platform provides duplex communication between applications running at endpoint devices and the network. It is a flexible platform that can be used to improve performance for various types of traffic. For low-level radio-resource management, when several network slices use the same RF front-end, the WNL team introduces a wireless hypervisor called AirHYPE. The goal of AirHYPE is to multiplex several data streams into a single stream, which is then passed to the physical RF front-end. This simple idea allows ARBAT to fulfill latency requirements for URLLC traffic by placing the URLLC processing slices as close to RF as possible and renting out RF front-end for other network slices that are less sensitive to latency.
To reduce network costs, ARBAT allows sharing network infrastructure between several service providers. This is possible because of Service Bridge – a smart interface between Infrastructure Operator and Service operator. ServiceBRIDGE allows provisioning of network services across multiple infrastructure domains, without the complexity associated with inter-domain interaction.
To summarize, ARBAT has many innovative features that are aimed at providing highly efficient QoE-aware communications in heterogeneous environments with low capital and operational expenses. Specifically, by following the virtualization paradigm and replacing the hierarchical Core Network and Radio Access Network with a Unified Cellular Network consisting of UNDs, we can easily bring the external data network closer to users, thereby reducing latency and enabling the URLLC use-case. At the same time, for highly efficient spectrum usage and operation with massive antennas, control functions can be deployed at a fewer number of central UNDs with higher computational capabilities. Moreover, the concept of UNDs allows ARBAT to both integrate legacy devices with hardware-defined PNFs, as well as make use of infrastructure resources for running various network functions efficiently. Tight communication between applications and the network via the xStream platform combined with the original multi-slice modular resource management aims to maximize network capacity for the provided QoE for different slices. XStream synchronizes network capabilities and application demands excluding computational-heavy nonoptimal and error-prone machine learning-based decisions on traffic characteristics and network capabilities. Non-isolated slicing paradigm avoids wasting of channel resources and allows maximizing user-perceived spectral efficiency, while the modular design of resource allocation allows running radio-resource schedulers that belong to different service operators. The latter together with enhanced MANO with ServiceBRIDGE simplifies multi-tenant orchestration. WNL team is in the process of fully implementing the ARBAT architecture and making it publicly available soon.
