Empirical study on how to model Cloud VR published in Open Journal of the Communications Society
The paper “How to Model Cloud VR: an Empirical Study of Features That Matter” authored by Eugene Korneev, Mikhail Liubogoshchev, Dmitry Bankov, and Evgeny Khorov has been published in IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society.
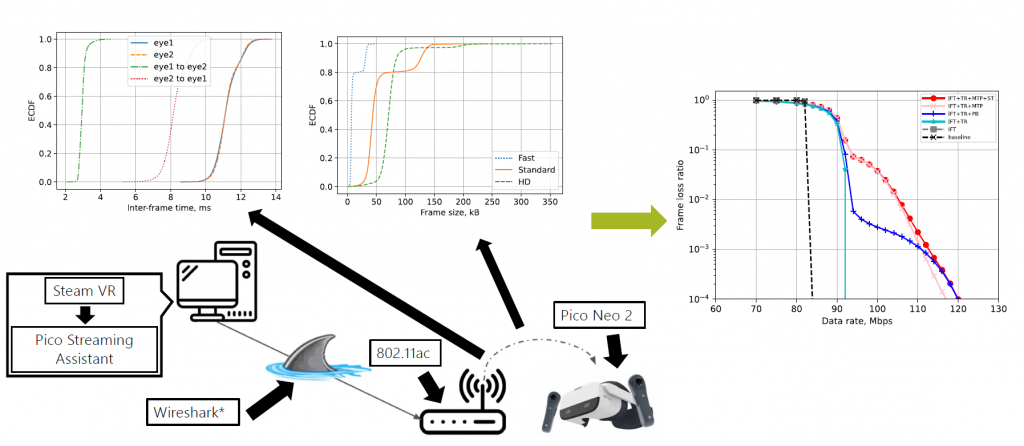
Interactive virtual reality (VR) applications require high-quality, real-time image rendering and display, which can be provided either with expensive high-end hardware in VR headsets, or with Cloud VR. The latter relies on offloading the computationally intensive rendering tasks to remote servers and thus requires much less computational resources on the client, but needs real-time reliable delivery of the VR traffic over the networks, which is a challenging task. To develop network solutions that can meet all the VR traffic requirements, researchers need a thorough and realistic model of VR traffic and of the impact of packet service on the quality of VR. Realistic VR Quality of Service (QoS) requirements are also required. This paper presents an experimental study of cloud VR traffic collected with an off-the-shelf Pico Neo 2 VR headset. The traffic properties were used to construct a novel VR application model that accounts for the VR application features that have the most significant impact on QoS.
The paper shows that the developed model provides accurate estimation of the effective VR bitrate while the 3GPP traffic model significantly underestimates it. Then the model is used to evaluate the benefits of intra-refresh video coding and adjusting video buffering at the VR headset according to motion-to-photon requirements. Finally, based on the revealed important features, the paper improves a VR bitrate adaptation algorithm.
The paper is published in IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, a first-quartile (Q1) journal with an Impact Factor of 6.3. This journal publishes studies dedicated to science, technology, applications and standards for information organization, collection and transfer using electronic, optical and wireless channels and networks.
